Pinene is a naturally occurring terpene often found in forests that smells like, you guessed it, pine trees. A terpene is one of several aromatic molecules that helps give plants their unique effects. Terpenes are found in the resinous glands of cannabis plants (trichomes) and contribute to chemovar’s distinct properties. It’s one of eight primary terpenes that often dominate cannabis flowers in North America.
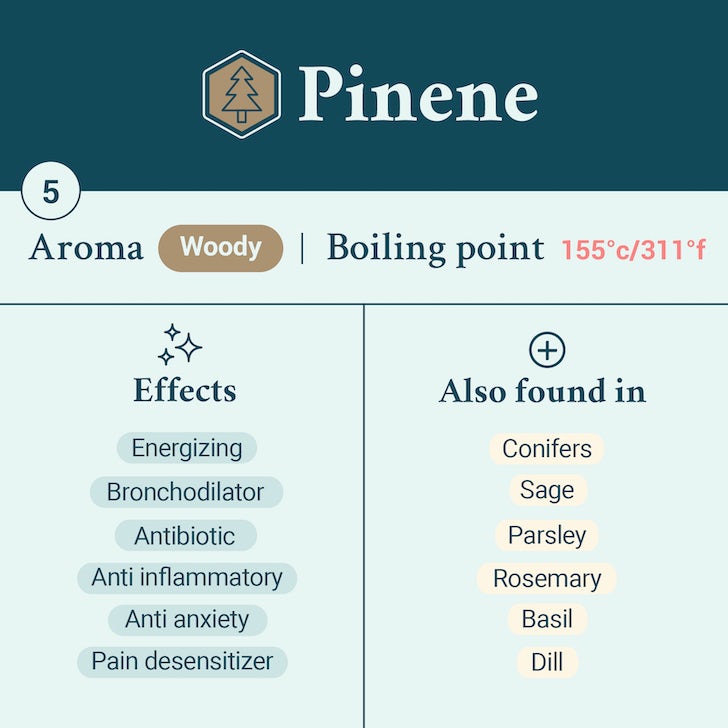
Pinene — specifically Alpha Pinene, or ????-Pinene — is the most abundant terpene in nature, and it is remarkable for many reasons. Pinene is an anti-inflammatory compound that acts as a bronchodilator and potent antimicrobial agent. It also has significant anticancer and anti-depressant properties and is thought to also act as a neuroprotectant that can counteract memory loss associated with THC. The range of medicinal properties of pinene suggests a potential application in conditions such as arthritis, dementia, asthma, acne, stress and cancer (particularly neuroblastoma, melanoma, and hepatic carcinoma).
Where is it found?
Pinene is abundant in forests with coniferous trees but can be found in many other plants and essential oils as well. Pinene is abundant in herbs such as rosemary, dill, oregano, thyme, tarragon, parsley and basil. It’s also commonly found in flowering Hyptis species, a type of flowering plant in the family Lamiaceae known as “bushmints.” You can also catch pinene in bay leaves, in orange peels and spices like nutmeg. Last but not least, you can commonly catch the scent of pinene in common household cleaning products.
How common is it in cannabis?
Cannabis chemovars and other plants can contain multiple kinds of Pinene. The two primary types are Alpha (a-Pinene) and Beta (b-Pinene).
While levels vary from chemovar to chemovar (and batch to batch), one chemovar that consistently ranks high in Pinene content is Blue Dream. One study analyzed 233 samples representing 30 cultivars to identify terpene content. They found Blue Dream “contained higher levels of α-pinene and β-pinene compared with all other cultivars in this study.” Other chemovars with high levels were: Purple Cream, Grape Ape, Purple Princess, Purple Urkle, Sherbert, Gelato, and Godfather.
You can also find a list of anecdotally known Canadian chemovars high in Pinene here. One of these is Aurora’s version of Blue Dream, dubbed “Ambition.” Its certificate of analysis reveals a terpene profile high in both Alpha and Beta Pinene.
If you are looking for a specific terpene in your cannabis chemovar, it is important to check its certificate of analysis, as a strain’s chemical makeup can vary from batch to batch, and grower to grower.
What are its effects? What else is it used for?
Pinene is associated with a calm, clear-headed feeling commonly associated with focus, and as such is often found in cannabis chemovars described as being more cerebral.
It has also been used as a therapeutic and medicinal agent for hundreds of years. Oil extracted from pine needles was used in traditional Chinese medicine as an anti-cancer treatment. Hyptis species high in Pinene have also been used in northern parts of Brazil to treat gastrointestinal issues. Mexican traditional medicine, too, utilizes Pinene via Litsea glaucescens (bay leaf family) to treat central nervous system disorders such as depression.
Today Pinene is being evaluated for a wide range of clinical applications. One of these includes a potential anti-ABV (infectious bronchitis virus) treatment. It is also used as an antibiotic resistance modulator and is being evaluated as a potential antitumor drug. It also has anxiolytic-like effects, helps the body modulate oxidative stress, and exhibits a protective effect against cell cytotoxicity.
References:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28826544/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/alpha-pinene
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24455984
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/797044/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22634841
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6920849/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22867633
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3165946/#b218
https://headachejournal.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/head.13345
https://genesandnutrition.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12263-019-0636-8
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4329611/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22867633
https://genesandnutrition.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12263-019-0636-8
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6920849/
https://cannigma.com/strains/blue-dream/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5436332/
https://medproducts.cdn.prismic.io/medproducts/271b42ff-b9e2-4152-ae94-5cd3748a0ccd_ambition-1104020000157.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25837931
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4329611/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22867633
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21350392
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6920849/
Sign up for bi-weekly updates, packed full of cannabis education, recipes, and tips. Your inbox will love it.

 Shop
Shop Support
Support















