If you enjoy the zesty, floral scent that can characterize select cannabis chemovars you’re likely to be a fan of β-Ocimene. It is a terpene found in a variety of plants as well as cannabis flowers. A terpene is one of several aromatic molecules that give plants their unique effects. Terpenes are found in the resinous glands of cannabis plants (trichomes) and contribute to chemovar’s distinct properties. Some plants with high β-Ocimene content include basil, mangoes, mint, orchids and members of the flowering plant family Lauraceae such as bay leaves.
As a monoterpene β-Ocimene comes in several different forms. These include α-Ocimene, cis-β-Ocimene, and trans-β-Ocimene. As such, Ocimene compounds are generally found in nature as mixtures of the various forms.
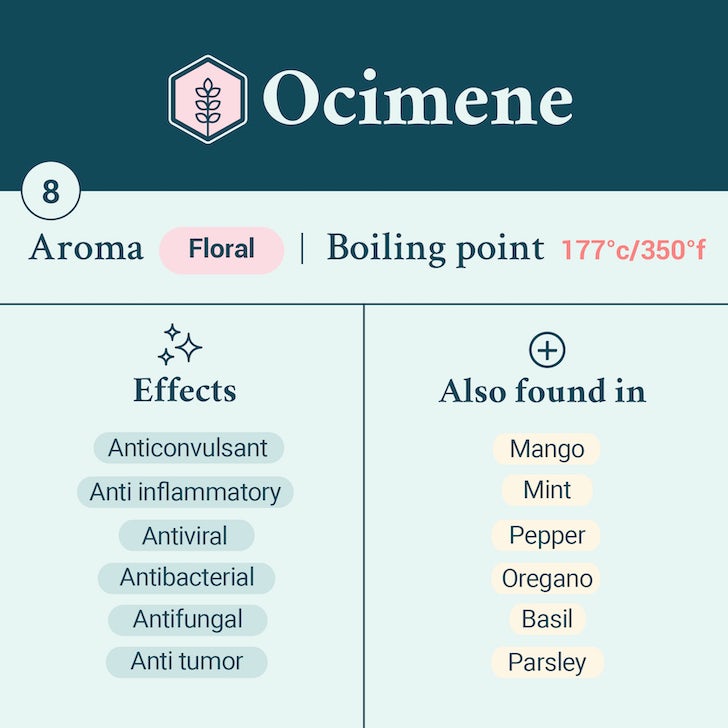
β-Ocimene’s scent is said to be a combination of floral citrus-y, woodsy, herbaceous and fresh notes. Like many other terpenes β-Ocimene is an effective insect repellent for many species. Ironically the E form is also used as a brood pheromone to socially regulate bee colonies.
What are its effects? What else is it used for?
β-Ocimene’s psychotropic effects have yet to be fully evaluated. That being said, the therapeutic properties of this terpene include its anticonvulsant, anti-viral, antifungal, and antioxidant abilities. These suggest potential application in inflammation, seizure-related conditions, such as epilepsy, and different types of cancer.
One 2008 study set out to analyze antiviral traits of essential oils in seven native Lebanonese species including Laurus nobilis. Researchers found that Laurus nobilis essential oils–a plant high in β-Ocimene content–exhibited inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV (a virus that causes respiratory illness) and HSV-1 (Herpes Simplex) replication.
A 2014 study examining the composition of Ferulago carduchorum essential oil, a member of the Apiaceae plant family native to Iran, found it was rich in β-ocimene. Those researchers also discovered that the Ferulago essential oil, “…had noticeable efficiency against Candida albicans,” a pathogenic yeast.
Another study dedicated to investigating the composition and anti-inflammatory potential of essential oils from C. unshiu flowers took place in 2014. Research revealed that C. unshiu flowers contained significant levels of several terpenes including β-Ocimene. They also found that the essential oil suppressed the production of inflammatory cytokines and concluded that, “CEO [C. unshiu flower] may be considered a potential anti-inflammatory candidate.”
Its antifungal activity was further reinforced in a 2015 study analyzing antifungal activity of the essential oil of Angelica major against several dermatophyte species.
How common is it in cannabis?
It’s likely that β-Ocimene is fairly ubiquitous in cannabis plants, though the extent to which this terpene is produced in each chemovar varies.
A 2017 research paper analyzing trichome production in the cannabis hemp variety ‘Finola’ identified β-ocimene as one of the primary compounds compromising Finola resin.
One study analyzed 233 samples representing 30 cultivars to identify terpene content. They found trans-Ocimene present in substantial amounts in the following chemovars: Strawberry Haze, Trainwreck, Purple Urkle and Purple Princess.
Though it’s important to note that there’s no clear standard for cannabis strains, two very distinct cannabis varieties can bear the same name since there’s no agreement about the exact chemical profile of any of them. And because chemovars can vary in terpene content from grower to grower and even batch to batch, it’s a good idea to check out a product’s certificate of analysis whenever possible to determine terpene profiles.
Where else is it found?
Because of its characteristically fresh and citrusy smell β-Ocimene is a popular ingredient in many cosmetic applications such as topical creams. You can find it in many fragrances/perfumes, home products, industrial products and cleaners such as air fresheners.
β-Ocimene is also a popular food additive that’s used in a wide variety of different products. These can include food colorings/flavorings, extracts, condiments and spices.
Many essential oils are also produced that contain significant amounts of β-Ocimene. These include oils extracted from Artemisia dracunculus (French tarragon), basil essential oil, black pepper oil, citrus-derived essential oils and Daucus carota L. (wild carrot family).
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2958837/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18357554
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26114148
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25576097
https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article%3Fid%3D10.1371/journal.pone.0173911
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5436332/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/ocimene
Sign up for bi-weekly updates, packed full of cannabis education, recipes, and tips. Your inbox will love it.

 Shop
Shop Support
Support
















