Medical marijuana: Legal
Recreational marijuana: Legal
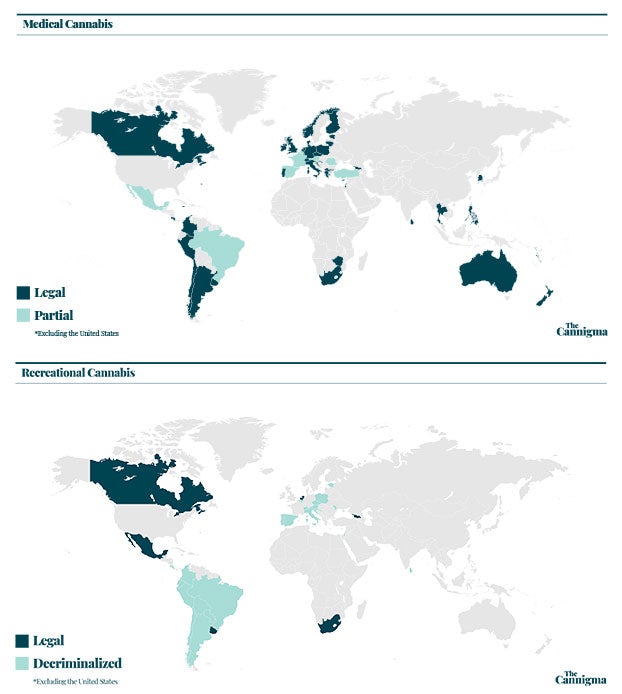
In 2018 Canada became the second country in the world after Uruguay to legalize marijuana for recreational adult use, and the first G7 country to do so. Medical cannabis has been legal since 2001.
Depending on the province or territory, Canadian law allows anyone over 19 years of age (21 in Quebec, 18 in Alberta) to possess cannabis. One can sell or distribute cannabis if authorized by the state.
Canadian law permits:
- Buy, possess (up to 30 grams), or use cannabis and cannabis products if you are over 18.
- Share up to 30 grams of dried cannabis or its equivalent with other adults
- Buy cannabis products from a provincial or territorial retailer
- Grow up to four plants per residence for personal use
- Sell edible cannabis, cannabis extracts and topicals from a licensed retailer
Possession, producing, or distributing cannabis outside of what the legal framework can result in a fine or a maximum penalty of up to 14 years imprisonment.
Canadian law bans:
- Products that are “appealing to youth”
- Packaging or labelling in a way that makes cannabis appealing to youth
- Self-service displays or sales, such as by way of vending machines
- Unauthorized promotion of cannabis products and services
- Transporting cannabis across the Canadian border for any purpose
➤ Cannabis laws around the world
History of marijuana legalization in Canada
The trial of an epileptic man who was arrested for growing marijuana to treat his epilepsy opened the door to legal medical marijuana in Canada. Under the ruling in R. v. Parker, people with a medical need had the right to possess marijuana for medical purposes. This led the Canadian government to pass the Marihuana Medical Access Regulations which since 2001 has allowed people to lawfully use and possess dried marijuana flower marijuana for medical purposes.
This legislation was followed in June 2013 by the Marihuana for Medical Purposes Regulations, which laid out the conditions for a commercial industry that can produce and distribute medical marijuana. In 2015, the government of Canada issued expectations to allow licensed produces to make and sell cannabis oil and cannabis flowers, as well as other cannabis products.

In April 2017, the Minister of Justice Jody Wilson-Raybould submitted to the House of Commons Bill C-45, which enacted the Cannabis Act, a new act that allows the possession of up to 30 grams of cannabis in public and the cultivation of up to 4 cannabis plants per private residence.
The Cannabis Act (also known as S.C. 2018) was later passed in 2018 in part to “provide for the licit production of cannabis to reduce illicit activities in relation to cannabis,” and reduce the criminal justice burden created by cannabis laws while providing “access to a quality-controlled supply of cannabis.”
Provincial/territorial regulations
The regulations surrounding cannabis and the sale, production, and distribution of cannabis products can differ by region in Canada.
- In seven different provinces and territories (British Columbia, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Northwest Territories, Prince Edward’s Island, Quebec, and Yukon), cannabis can be purchased online or at government operated stores.
- In Saskatchewan, Manitoba, Newfoundland and Labrador, and Ontario, purchases can be made at private licensed in-person and online stores. In Nunavut, purchases can be made only at a government-operated online stores or by phone.
- In the Northwest Territories, cannabis sales are currently only allowed in government-operated liquor stores.
- In Alberta the legal age for cannabis is 18 and in Quebec it is 21. In all other provinces and territories the legal age is 19.
- In every province and territory, the limit on public possession is 30 grams of dried cannabis “or equivalent.”
- In Manitoba and Quebec, home cultivation is not allowed.
Public use laws:
- In Manitoba, New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nunavut, Ontario, Yukon, and Saskatchewan, cannabis can only be smoked on private property or inside private residences.
- In Ontario, British Columbia, and Alberta, the law allows the smoking of cannabis in places where smoking cigarettes is allowed.
- In other provinces and territories some exceptions are made for nature areas and other public spaces.
Where to purchase cannabis in Canada
Is weed legal in Canada for purchase? Cannabis purchases are allowed in Canada according to the regulations in the province or territory in question. There are currently physical cannabis storefronts in all provinces and territories except for Nunavut, where the Nunavut Liquor and Cannabis Commission sells cannabis remotely by way of online or phone orders, or in state-run liquor stores.
The cannabis retail stores are a mix of government-run retail shops or private stores, and some are a mix of the two.
Alberta currently has the most licensed cannabis stores — at nearly 500 — while Ontario, Canada’s most populous province, has only a few dozen.
Throughout the country, provinces and territories have adopted regulations regarding how and where they can sell cannabis in order to deal with the social distancing requirements of the COVID-19 outbreak.

How to qualify for medical marijuana in Canada
The current law governing medical marijuana in Canada is the “Access to Cannabis for Medical Purpose Regulations.”
Patients can qualify for medical cannabis in Canada by having their healthcare practitioner fill out the following form.
The law allows healthcare practitioners to provide an individual in their care with a medical document or written order allowing them to use cannabis for medical purposes, or to administer it to the patient themselves.
Approval is given for up to one year and must be extended afterwards.
Under the Cannabis Act, patients who qualify for medical marijuana — or an adult caretaker — can legally be in possession of either up to 150 grams of dried cannabis or 30-times the daily quantity of dried cannabis allowed in their registration document.
Adults over the age of 18 who reside in Canada and have not been convicted of a cannabis related offense can apply to produce cannabis for their own medical purposes. In order to determine how much, Health Canada has provided an online calendar. It takes into account your daily authorized usage and whether or not it will be an inside or outside grow.
For instance, if you are allowed 3 grams of cannabis a day and would like to grow outdoors, you can legally grow six plants and have 1,125 grams in storage. If you would like to grow both indoor and outdoor and are allowed 5 grams per day, you can have 19 indoor plants, five outdoor plants, and 1,875 grams in storage.
In Canada you can receive medical cannabis for any condition or symptoms approved by your personal healthcare practitioner.
Common indications include:
- Multiple sclerosis-related muscle spasms
- Nausea and vomiting from chemotherapy
- Chronic neuropathic pain
- Insomnia and depression
- Appetite and weight issues due to cancer or HIV/AIDS
- Symptoms encountered during palliative or end-of-life care
Join The Cannigma Directory
Cannabis taxes in Canada
Canada requires a federal excise duty to be paid by cannabis producers when their products are delivered to a purchaser (such as a licensed dispensary). The excise stamp must appear on all cannabis products.
Cannabis customers must pay the Goods and Services Tax (GST) and the Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) when making a cannabis purchase. Depending on the province or territory, this can range from 5% to 15%.
Advocates have pushed for removing the sales tax for medical cannabis purchases, which can add roughly 10% to the cost of the medicine.
Traveling with cannabis in Canada
If you are flying within Canada you are allowed to bring your cannabis with you, up to the legal limit of 30 grams. Cannabis oil is allowed up to 100ml. If you wish to exceed these limits you will need to show proof of a legal medical marijuana permit. You are not allowed to carry cannabis onto the flight if it will cross into another country.
It is illegal to transport cannabis across the border into or out of Canada without declaring it, no matter the quantity or type of license.
Sign up for bi-weekly updates, packed full of cannabis education, recipes, and tips. Your inbox will love it.

 Shop
Shop Support
Support